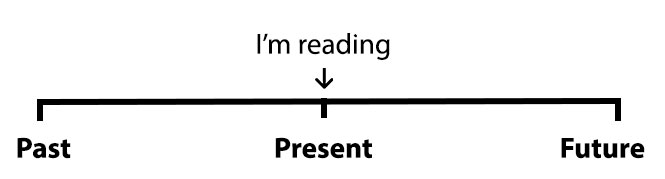
In this article, we are going to learn Simple Present Continuous Grammar in English which is one of the most important tenses in English. What is simple present continuous and when do we use that?
Whenever we want to talk about actions or situations that are happening right now, we use the present continuous (or also called present progressive) tense.
Please be quiet. I’m studying. (I’m studying now.)
What are you doing? Actually, I’m watching TV.
We can not go out right now, it’s raining.
Table of Contents
The present continuous
The structure of the present continuous is:
To be verb (am, is, are) + verb +ing
| I am reading. | I’m reading. |
| You are reading. | You’re reading. |
| He/She/It is reading. | He’s/She’s/It’s reading. |
| We are reading. | We’re reading. |
| They are reading. | They’re reading. |
She’s dancing.
They’re eating lunch.
The structure
To most of the verbs, we add (ing) to the base form of the verb.
- Read 》reading
- Work 》working
- Talk 》talking
- Stand 》standing
Verbs that end in _e (make/ write/ drive etc.): drop the “e” and add “ing”.
- Make 》making
- Write 》writing
- Come 》coming
- Dance 》dancing
For verbs that end in _ie: we remove the _ie and then add _ying.
- Lie 》lying
- Die 》dying
- Tie 》tying
For verbs that end in “n”, “t”, “p”, “m” and “s”: double the letters and then add”ing”.
- Run 》running
- Sit 》sitting
- Swim 》swimming
- Pass》passing
- Stop 》stopping
Questions and negatives
For making negative sentences we add (not) after the “to be” verb.
| Positive | Negative | Contracted |
| I’m reading. | I’m not reading. | – |
| You’re reading. | You’re not reading. | You aren’t reading. |
| He’s/She’s/It’s reading. | He’s/She’s/It’s not reading. | He/She/It isn’t reading. |
| We’re reading. | We’re not reading. | We aren’t reading. |
| They’re reading. | They’re not reading. | They aren’t reading. |
He isn’t reading a book.
We aren’t working right now.
Questions
To make a “Yes/No” question, we change the place of the subject and the “to be” verb (am, is, are).
| Positive | Question |
| I am reading. | Am I reading? |
| You are reading. | Are you reading? |
| He/She/It is reading. | Is he/she/it reading? |
| We are reading. | Are we reading? |
| They are reading. | Are they reading? |
Are you studying? Yes, I am. (Not: yes, I’m)
To be verb + subject+ verb + ing
Are you crying? Yes, I am/ No, I’m not.
Information questions (WH questions)
To make a “WH” question or also called an information question, the structure is like this:
Wh + to be verb + subject + verb + ing
What are you doing? I’m eating dinner.
When is she going? She’s going at 5:00 p.m.
Contractions
Positive statements:
- I am working 》 I’m working
- She/he/it is working 》She’s/he’s/it’s working
- We/you/they are working 》We’re/you’re/they’re working
Negatives:
- I’m eating 》I’m not eating.
- She/he/it’s eating 》she/he/it isn’t eating.
- We/you/they’re eating 》we/you/they aren’t eating.
Note: in Yes/No questions:
Are you dancing? Yes, I am/ No, I’m not. (Not: Yes, I’m)
Is he drinking tea? Yes, he is/ No, he isn’t. (Not: Yes, he’s)
For “YES” we never use contractions!
Usage
It is used to talk about actions or situations that are happening right now.
I’m watching TV.
They aren’t playing basketball.
Is she studying? No, she isn’t. She’s dancing.
What is John doing? He’s washing his car.
Intermediate Points
What is present continuous tense? We use the present continuous to talk about temporary actions and situations that are ongoing or (around now).
Please be quiet, I’m studying. (I’m studying right now)
We can’t go camping. It’s snowing.
Present continuous VS present simple
Present continuous: something that we do right now, at the time of speaking.
I’m reading a book.
Present simple: in general, all the time, or sometimes.
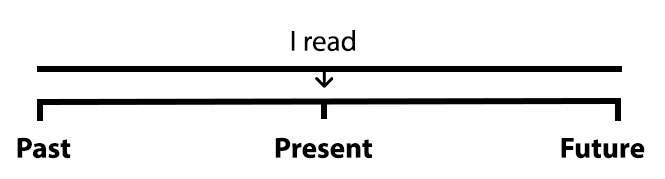
I read books.
Study this example situation:
John is reading a book.
He’s not cooking food. But John is a chef.
He’s good at cooking and he cooks delicious food.
John always cooks food.
But he isn’t cooking food right now.
Is he cooking food? No, he isn’t. (Present continuous)
Does he cook food? Yes, he does. (Present simple)
Periods around now
We can use the present continuous with “today, this week, this month, this year, etc”.
Are you studying for your exams this week?
My son isn’t doing well at school this year.
Changes happening around now
When we want to talk about changes happening around now, we can use the present continuous. Especially with these verbs:
- Get
- change
- become
- increase
- rise
- fall
- grow
- improve
- begin
- start
At first, I didn’t like to study English, but I’m beginning to love it now. (Not: I begin …)
Air pollution is increasing very fast. (Not: the air pollution increases …)
Repeated actions
The present continuous can refer to repeated actions and events which are just happening around the present time.
I’m working a lot these days.
Nowadays he’s trying to help his wife with the chores.
Talking about the future
We use the present continuous for future actions and events which have some present realities. This is most common when we talk about fixed plans in which the time and place have been decided.
Where are you going tomorrow morning?
He’s passing the days in London next week.
Permanent situations
We do not use the present continuous to talk about things that happen repeatedly, regularly or all the time. Compare:
My parents live in London.
My brother’s living in London for a couple of months.
She always drinks two cups of tea.
She’s drinking tea on the balcony.
Note: Some verbs are not used in continuous forms even if the meaning is about the present and (around now). These verbs are:
- like
- prefer
- love
- hate
- want
- need
- know
- mean
- understand
- believe
- remember
- forget
- depend
- contain
- etc.
I like this coffee. (Not: I’m liking….)
This library contains about 6000 books. (Not: this library is containing …)
Stories
Both present tenses are often used to tell stories (but informally). The simple present is used for tge events that happen one after another. The present continuous is used for things that are already happening when the story starts or when continues through the story.
The prince goes to his bedroom and he looks out the garden from the window and hw sees Cinderella. She’s wearing a long dress with high heels and also wearing her hair in a ponytail style…
Advanced Points
What is present continuous? The present continuous is used to talk about ongoing actions in the present time at the time of speaking (now) or around now. In other words:
I’m doing something: I’m in the middle of doing it; I’ve started doing it and I haven’t finished.
Please don’t make so much noise, your brother’s sleeping.
Are we meeting tonight?
Long-lasting changes
We use the present continuous to talk about changes, even if they’re from a long time ago.
The climate is getting colder. (Not: the climate gets colder.)
“The epidemic is expanding.” doctors said.
[/ex]
Frequent actions
We can use the present continuous with “always, forever, constantly, etc” to talk about something that happens again and again.
They’re always fighting together.
She’s constantly arguing with her mother-in-law!
Present continuous VS present simple
Present continuous: We use the present continuous for things happening at or around the present time. The action is not complete.
The water is boiling. Please turn it off.
And it is used to talk about temporary situations.
I’m living with my parents at the moment.
Present simple: We use the present simple in general or for the things that happen regularly and all the time.
Water boils at 100 degrees Celsius.
And it is used to talk about permanent situations.
I live with my parents. I’ve lived with them all my life.
Think:
When “think” means “believe” or “have an opinion” we do not use the present continuous.
I think she’s from Brazil. (Not: I’m thinking …)
He is proud VS he’s being proud
He’s being = He’s behaving
Why he’s being so proud in the meeting?
(Being proud = behaving like that at the moment)
He thinks he’s the best. He’s really proud.
(He’s proud generally, not just at the moment)
Temporary Situations: state verbs
We use the present continuous with some state verbs (like, look, love, sound, etc) when we want to emphasize that the situation is temporary or for a period of time around the present time. Compare:
Ellen plays with children very often but the children love playing with him.
Ellen’s playing with the children right now. The children are loving playing with him.
Note: Some state verbs are rarely used with the present continuous: doubt/own/consist of/believe etc.
State, action
Some verbs have different meanings according to their usage. (When they’re used to talk about states or when they’re used to talk about actions.) If they’re used as their state meaning we use the simple present and if they’re used as their action meaning we use the present continuous.
Do you think it’s true? (Think = state about an idea.)
I’m thinking about tomorrow’s meeting. (Think = action = consider something.)
Note: the verb “consider” if it means “think carefully about something” is only used with the present continuous, not the present simple.
She’s considering taking new medicines for her heart attack. (Not: she considers taking …)
Note: some verbs like apologize/deny/guarantee/promise/suggest etc have a similar meaning with either the present simple or present continuous in NEGATIVE sentences.
I don’t suggest/I’m not suggesting taking these medicines, but mom said it would be okay.
Wonder
If we want to be especially friendly or polite, we can use the present (or past) continuous rather than the present (or past) simple with the verb WONDER.
You said that you won the match. I’m just wondering/I was just wondering how you could tell us a lie? (more polite than “I just wonder …”)
In this article, we learned one of the useful and important grammar in English which is used a lot in daily speaking. We hope it’s useful for you. If you have any questions about it, just leave a comment for us.
You can also check out the English Grammar page to read other grammatical articles.
